How to Store Wheat: Essential Tips for Farmers
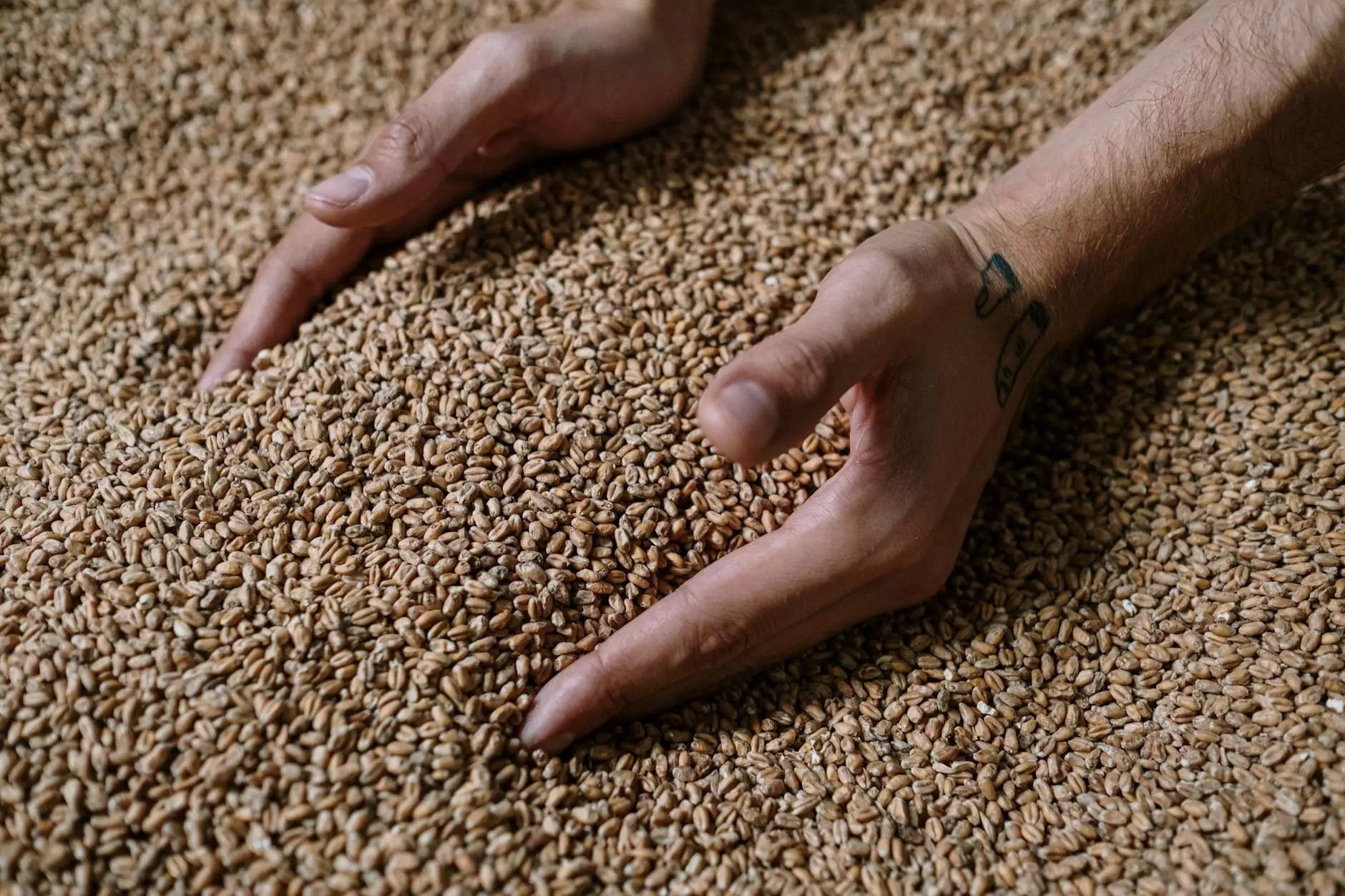

Wheat is one of the most vital grains in the world, providing sustenance for billions of people. Proper storage is critical to ensure that wheat retains its quality and nutritional value over time. Whether you are a large-scale farmer or a small-scale producer, understanding how to store wheat is essential for maximizing your investment and minimizing loss. This comprehensive guide will delve into effective strategies, best practices, and expert advice on storing wheat efficiently.
Importance of Proper Wheat Storage
Storing wheat correctly has several benefits:
- Preservation of quality: Proper storage helps maintain the quality of wheat, including its flavor, texture, and nutritional content.
- Prevention of pests and diseases: Effective storage practices mitigate the risks of infestations and spoilage from mold or bacteria.
- Cost-effectiveness: By reducing losses through spoilage and waste, you can save money in the long run.
- Maintain market value: Well-stored wheat has a higher market value compared to poorly maintained grains.
Understanding Wheat Types and Their Storage Needs
Before diving into how to store wheat, it's important to understand the different types of wheat and their specific storage requirements.
Types of Wheat
Wheat is classified into several categories, the most common being:
- Hard Red Winter Wheat: High in protein, ideal for bread-making.
- Soft Red Winter Wheat: Lower in protein, used for cakes and pastries.
- Hard Red Spring Wheat: High-gluten content, perfect for artisan bread.
- Durum Wheat: Used primarily for pasta and semolina.
- Soft White Wheat: Best for pastries and crackers.
Best Practices for Storing Wheat
When considering how to store wheat, follow these best practices to ensure optimal results:
1. Choose the Right Storage Location
The storage location plays a pivotal role in preserving wheat quality. Here are some factors to consider:
- Temperature: Keep storage areas at a cool, stable temperature, ideally below 70°F (21°C).
- Humidity: Maintain low humidity levels (around 20% or less) to prevent mold growth.
- Avoid direct sunlight: Store wheat in a dark place to avoid degradation from UV rays.
2. Select Appropriate Storage Containers
The type of container you use for storing wheat can significantly impact its longevity:
- Grain Bins: Use grain bins made of weather-resistant materials for larger quantities.
- Food-Grade Buckets: Ideal for smaller amounts, ensure they are sealed tightly.
- Vacuum Sealing: Vacuum seal packages for long-term storage; this is especially effective for home storage.
3. Properly Prepare Wheat for Storage
Before placing wheat into storage, follow these preparation steps:
- Cleaning: Remove any foreign materials such as chaff and debris, as they can harbor pests.
- Drying: Ensure wheat is thoroughly dried to a moisture content below 13% to prevent spoilage.
- Inspecting: Regularly check for signs of pests or spoilage before and during storage.
Pest Control in Wheat Storage
One of the biggest threats to stored wheat is pest infestations. Effective pest control is crucial in understanding how to store wheat properly. Here are several strategies:
1. Monitor Regularly
Conduct routine inspections of stored wheat. Look for signs of pests, including:
- Webbing: This indicates spider infestations.
- Frass (insect droppings): Presence of frass could point to grain weevils.
- Chewed grains: Evidence of damaged grains suggests larger pest infestations.
2. Use Natural Deterrents
Consider using natural pest deterrents such as:
- Boric Acid: Effective against common grain pests.
- Essential Oils: Oils like peppermint and clove can deter insects.
3. Implement Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Integrate several pest control methods for effective management, including:
- Sanitation: Keep storage areas clean and free from grain spillage.
- Biological controls: Introduce natural predators to control pest populations.
- Chemical controls: Use chemicals responsibly and only as a last resort.
Long-Term Wheat Storage Techniques
For farmers looking at long-term storage options, consider the following:
1. Using Cold Storage
Cold storage facilities provide optimal conditions for long-term wheat preservation. Ensure that:
- The temperature remains consistently below 40°F (4°C).
- Humidity levels are monitored and controlled to prevent moisture-related spoilage.
2. Controlled Atmosphere Storage
This method involves modifying the environment within the storage container:
- Reducing Oxygen: Use inert gas systems to displace oxygen and create an environment that inhibits pest development.
- Managing Temperature and Humidity: Constant monitoring ensures that both remain stable, preserving the wheat’s integrity.
Emergency Storage Solutions
Sometimes, immediate storage solutions may be necessary due to unforeseen circumstances. Here are some quick tips:
- Plastic Wrap: Wrap smaller amounts of wheat in plastic wrap to protect from moisture and pests.
- Temporary Bins: Utilize bins or containers from existing supplies, ensuring they are cleaned and dry.
Conclusion
Understanding how to store wheat effectively is crucial for any farmer aiming to maintain the quality and value of their grain. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your wheat remains safe from pests and spoilage, ultimately leading to greater profitability and sustainability in your farming operations. Remember, investing time and resources into proper storage can make all the difference in the quality of your yield and your overall success in the agricultural sector.
For more information and expert advice on agricultural practices, be sure to visit tsgcinc.com.