The Art and Science of Architecture Model Making

Architecture model making is a fundamental aspect of the architectural design process, playing a crucial role in transforming abstract concepts into tangible representations. This process not only facilitates communication between architects, clients, and stakeholders but also allows for iterative refinements, clarity, and an enriched understanding of spatial relationships. In this article, we will delve deep into the nuances of architecture model making, its various applications, and why it is indispensable in the field of architecture.
Understanding Architecture Model Making
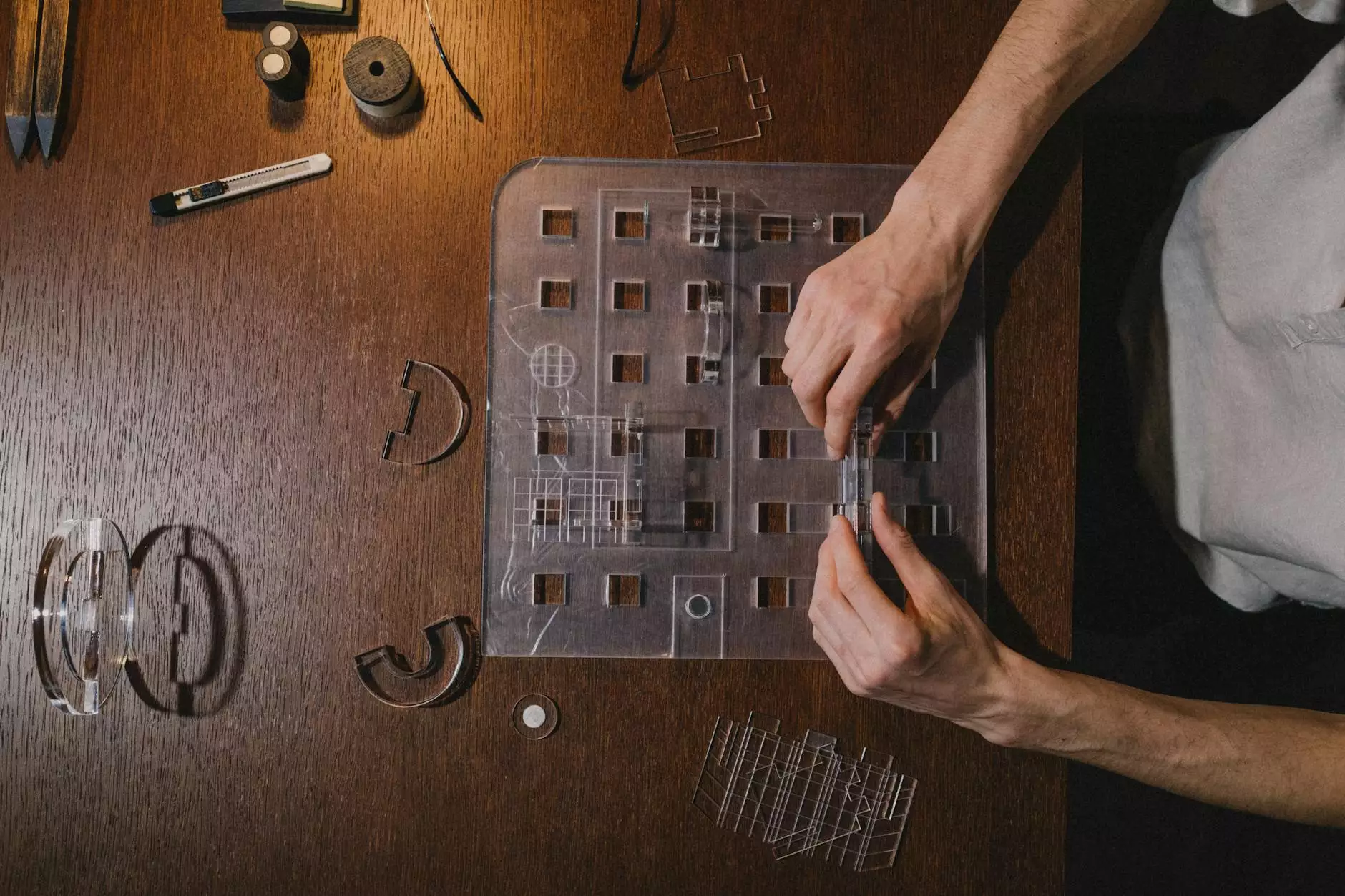
At its core, architecture model making is the craft of creating physical models that represent the proposed design of a building or structure. These models range from highly detailed, full-scale representations to simplified, conceptual models that capture the essence of a design idea. The process not only involves artistic skills but also technical knowledge of materials and construction methodologies.
The Importance of Physical Models in Architecture
Physical scale models serve several critical purposes:
- Visual Communication: Models provide a 3D perspective that enhances understanding, enabling architects to convey their vision effectively to clients and collaborators.
- Design Evaluation: By creating a model, architects can evaluate the design's aesthetics and functionality, identifying any potential flaws or areas for improvement before construction begins.
- Client Engagement: Engaging clients through model presentations fosters collaboration and helps to align expectations, resulting in a more satisfactory outcome.
- Marketing Tool: Detailed physical models are often used in marketing materials to attract investors or buyers by showcasing the project in an appealing manner.
Types of Architectural Models
Architecture model making encompasses various types of models, each serving specific purposes:
1. Conceptual Models
Conceptual models are quick representations used primarily during the early design phase. They are often made from foam or cardboard, allowing architects to convey ideas rapidly and explore various design options.
2. Presentation Models
These models are more refined and detailed, intended for meetings with clients or presentations to stakeholders. They are usually crafted from materials like acrylic, wood, or high-quality paper, showcasing the design's aesthetics and intricate details.
3. Construction Models
Construction models are built to scale and often used on-site during the building process. These models include specific details and materials that inform contractors about the construction methods and sequence.
4. Structural Models
These models focus on the structural components of a building, demonstrating how the various elements work together to support the design. Structural models are vital for engineers to evaluate the feasibility of the design.
Materials Used in Architecture Model Making
The choice of materials in architecture model making can significantly impact the model's appearance and functionality. Common materials include:
- Wood: Ideal for detailed models due to its workability and aesthetic appeal.
- Foam Board: Lightweight and easy to manipulate, perfect for conceptual models.
- Acrylic: Used for transparent components, enhancing the model’s visual aspects.
- Cardboard: Cost-effective and readily available, suitable for quick prototypes.
- 3D Printed Materials: Increasingly popular for intricate details, allowing for complex shapes and designs.
The Process of Architecture Model Making
The process of creating an architectural model involves several key steps:
1. Concept Development
It all begins with understanding the design's vision and concept. Architects often sketch ideas and discuss them with stakeholders before committing to a particular model.
2. Material Selection
Choose appropriate materials that align with the model's purpose. Considerations include durability, aesthetic qualities, and the level of detail required.
3. Scale and Dimensioning
Establish a scale for the model, ensuring proportions accurately reflect the proposed design. This is crucial, especially for presentation models where viewer perception is key.
4. Construction
Using tools and techniques specific to the chosen materials, the architect or model maker assembles the model, paying close attention to detail and accuracy.
5. Finishing Touches
Final touches may include painting, texturing, and landscaping the model to provide a sense of realism and context.
Technology's Role in Architecture Model Making
With the advent of technology, architecture model making has transformed significantly. Digital tools and 3D printing have introduced new capabilities:
1. CAD Software
Architecture design software like AutoCAD and Revit allow architects to create precise digital models that can easily be converted into physical representations.
2. 3D Printing
This technology enables the production of highly intricate models that would be time-consuming and challenging to create manually. It allows for customization and rapid prototyping, enhancing the model-making process.
3. Virtual Reality (VR)
VR tools can create immersive experiences that allow stakeholders to explore the design before it is built, providing more valuable feedback and insights.
Best Practices for Effective Architecture Model Making
To maximize the effectiveness of architecture model making, consider the following best practices:
- Collaborate Early: Include all stakeholders during the model-making process to ensure alignment of concepts and goals.
- Iterate Designs: Use models to explore several design iterations quickly, allowing for rapid problem solving.
- Focus on Details: Attention to detail enhances the model's realism and provides a greater understanding of the final product.
- Maintain Flexibility: Be willing to adapt the model based on feedback from clients or team members.
- Document the Process: Keep a record of the model-making process for future reference and learning.
The Future of Architecture Model Making
As the architectural landscape continues to evolve, so does the practice of architecture model making. Innovations in materials, tools, and techniques promise to shape the future of architectural design.
Incorporating sustainable practices and environmentally friendly materials will become increasingly important. As architects face global challenges like climate change, models that represent energy-efficient designs and sustainable practices will be crucial.
Furthermore, integrating augmented reality (AR) with physical models could revolutionize how clients view designs, merging the tangible with the digital and enhancing the overall communication of ideas.
Conclusion
In summary, architecture model making is not merely a routine part of the architectural process; it is a pivotal element that enriches the craft of architecture. Through innovative techniques, effective communication, and a commitment to detail and quality, architects can utilize model making as a powerful tool to bring their visions to life.
As architects continue to embrace new technologies and sustainable practices, the importance of quality model making will only grow, ensuring that every project not only meets aesthetic standards but also addresses functionality, efficiency, and environmental impact.
By understanding the multifaceted role of architecture model making, architects at architectural-model.com are well-positioned to push the boundaries of design and innovation, creating spaces that resonate with beauty and purpose.